+91 9987398021 / +91 8433795981
Our Services
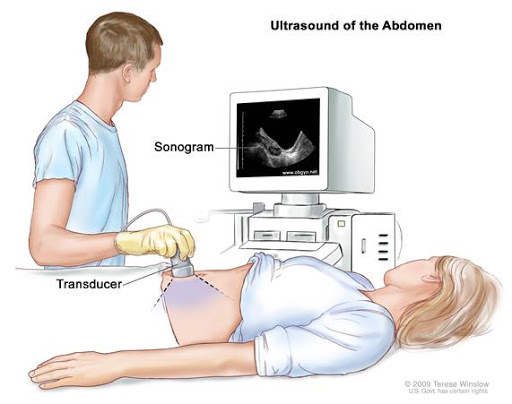
Sonography
Sonography is a diagnostic medical test that uses high-frequency sound waves—also called ultrasound waves—to bounce off of structures in the body and create an image. The test is often referred to simply as an ultrasound or as a sonogram.
Sonography uses a device called a transducer to send out ultrasound waves and listen for the echo. A computer translates the ultrasound waves into an image. A trained technician can see, measure, and identify structures in the image. A specially trained physician then reads the images to help diagnose medical conditions.
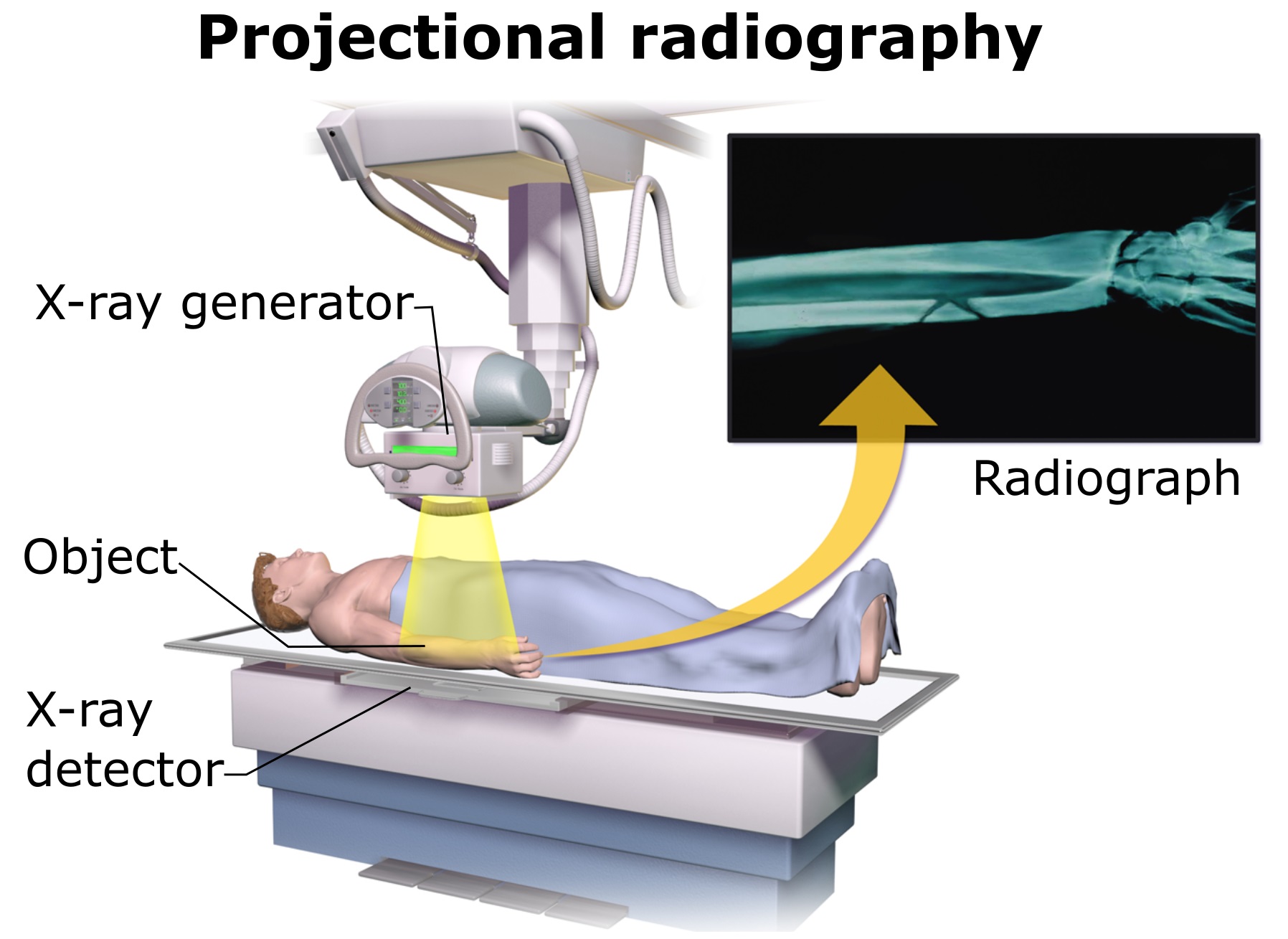
Digital X-Ray
Radiography with X-ray is the starting point for diagnosing or screening of a variety of health issues, including pneumonia. X-ray technology is increasingly easily available to the medical community due to its low cost. It’s noninvasive, relatively harmless, and quickly produces the images we need to be able to diagnose issues effectively.
Traditional X-rays have been around since the early 1900s, using film to capture images of the body’s internal structures. With the addition of computer technology, digital radiography has become a much more efficient, cost effective, and an even safer method of producing diagnostic images
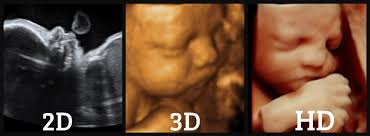
3D/4D Sonography
Like regular ultrasounds, 3D and 4D ultrasounds use sound waves to create an image of your baby in your womb. What's different is that 3D ultrasounds create a three-dimensional image of your baby, while 4D ultrasounds create a live video effect, like a movie -- you can watch your baby smile or yawn.
Parents often want 3D and 4D ultrasounds. They let you see your baby's face for the first time. Some doctors like 3D and 4D ultrasounds because they can show certain birth defects, such as cleft palate, that might not show up on a standard ultrasound.
Colour Doppler
A Doppler ultrasound is an imaging test that uses sound waves to show blood moving through blood vessels. A regular ultrasound also uses sound waves to create images of structures inside the body, but it can't show blood flow.
Doppler ultrasound works by measuring sound waves that are reflected from moving objects, such as red blood cells. This is known as the Doppler effect.

Mammography
A mammogram is an X-ray picture of the breast. Doctors use a mammogram to look for early signs of breast cancer. Regular mammograms are the best tests doctors have to find breast cancer early, sometimes up to three years before it can be felt.
You will stand in front of a special X-ray machine. A technologist will place your breast on a plastic plate. Another plate will firmly press your breast from above. The plates will flatten the breast, holding it still while the X-ray is being taken. You will feel some pressure. The steps are repeated to make a side view of the breast. The other breast will be X-rayed in the same way. You will then wait while the technologist checks the four X-rays to make sure the pictures do not need to be re-done. Keep in mind that the technologist cannot tell you the results of your mammogram. Each woman’s mammogram may look a little different because all breasts are a little different.
2D Echocardiography
The heart in your body pumps blood and the vascular system takes it to all the organs. Together they form the cardiovascular system. A healthy lifestyle, proper nutritious diet and regular exercise is much needed to keep your heart healthy, more so, as age progresses. Keeping a check on your heart’s health at regular intervals is also imperative to prevent its dysfunctioning.
Being consistent with your health checkups can help you in leading a happy & healthy life and thereby preventing major sudden-medical costs and trauma.

ECG
An electrocardiogram — abbreviated as EKG or ECG — is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat. With each beat, an electrical impulse (or “wave”) travels through the heart. This wave causes the muscle to squeeze and pump blood from the heart. A normal heartbeat on ECG will show the timing of the top and lower chambers.
The right and left atria or upper chambers make the first wave called a “P wave" — following a flat line when the electrical impulse goes to the bottom chambers. The right and left bottom chambers or ventricles make the next wave called a “QRS complex." The final wave or “T wave” represents electrical recovery or return to a resting state for the ventricles.

Pathology
Pathology is a branch of medical science primarily concerning the cause, origin and nature of disease. It involves the examination of tissues, organs, bodily fluids and autopsies in order to study and diagnose disease.
Currently, pathology can be divided into eight main areas, depending on the types of methods used or the types of diseases examined. These different disciplines are described below.
General pathology, Anatomical pathology, Clinical pathology, Chemical Pathology or Biochemistry, Genetics, Hematology, Immunology, Microbiology
